LiFi: Lighting Up the Future of Connectivity
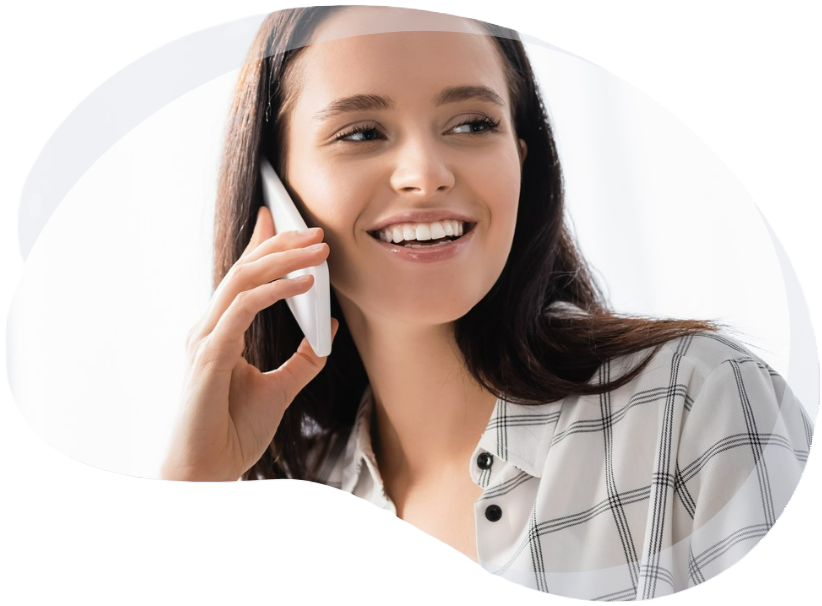
Experience fast, secure, and efficient connectivity with LiFi. Enjoy ultra-low latency, zero EMF radiation, and superior connectivity for a revolutionary online experience.
Powering the Digital Tomorrow
LiFi redefines digital communication with speeds up to 100 times faster than WiFi, offering unparalleled data transmission, security, and efficiency. This technology marks the start of a new era in robust wireless connections.
At LiFi.co, our mission is to bring LiFi’s potential into the practical world. We specialize in delivering innovative LiFi solutions that cater to both individual tech enthusiasts and organizations seeking to enhance their connectivity. Our focus is on providing secure, fast, and reliable wireless communication options that meet the demands of today’s digital landscape. Join us as we make this cutting-edge technology accessible and transform how the world connects.
As Featured By
Introducing the LiFiMAX Compact
Discover the future of wireless connectivity with the LiFiMAX Compact. This groundbreaking device offers blazing-fast speeds, ultra-low latency, and the capacity for multiple users to connect simultaneously, setting a new standard in the realm of internet technology. Its intuitive plug-and-play setup ensures easy installation, seamlessly integrating into any home or office environment.
The LiFiMAX Compact is not just about speed; it’s about elevating your entire online experience. With its advanced technology, you can say goodbye to buffering and hello to smooth, uninterrupted access. Available for a limited time at an exclusive discount, the LiFiMAX Compact is your gateway to a revolutionary internet experience. Upgrade your connectivity today with the LiFiMAX Compact!
Discover LiFi’s Advantages
Experience Light-Powered Connectivity
Dive into the transformative world of LiFi, where light becomes the cornerstone of digital communication. This innovative technology, harnessing the power of light for data transmission, outshines traditional WiFi with its speed, security, and efficiency. LiFi is not just a faster internet solution; it’s a leap towards a more connected, secure digital era.
LiFi finds diverse applications across sectors like healthcare, aviation, and education, providing reliable, high-speed internet. LiFi promises a sustainable, efficient future in digital connectivity. Join us in embracing a brighter, more connected world with LiFi.
Navigate the World of LiFi
A Spectrum of Possibilities
LiFi stands at the forefront of the wireless revolution, offering a sustainable and efficient solution to our ever-increasing data demands. By harnessing the potential of the light spectrum, LiFi transcends traditional communication barriers, paving the way for a brighter, more connected world. LiFi represents more than a technological leap; it’s a beacon of innovation, using light for high-speed, secure, and reliable data transmission.
If you’d like to delve deeper into LiFi, our eBook “LiFi Unbound” is a must-read. It offers a comprehensive look into LiFi technology, its applications, and future possibilities. This eBook is perfect for everyone, from tech enthusiasts to industry professionals, providing updated insights and practical strategies. Download it now for free for a limited time.
LiFi applications
Discover Our Products
LiFi in The News
“Li-Fi and Wi-Fi could greatly complement each other, and release the full potential of technologies such as the Internet of Things, and virtual reality and augmented reality.”

“Li-Fi is said to deliver faster, more reliable wireless communications with unparalleled security compared to conventional technologies such as Wi-Fi and 5G.”

“Speeds up to a ridiculous 224GB/s are promised by Li-Fi companies or the equivalent of downloading 18 HD movies every second.”
LiFi Blog
WiFi Security Vulnerabilities vs. LiFi: A Comparative Analysis
The Hidden Dangers of WiFi In today's digital age, WiFi has become a staple in households and businesses worldwide. However, beneath the convenience of wireless connectivity lies a plethora of security vulnerabilities that pose significant risks to users. One of the...
LiFi: A Game Changer for Remote Work
In the dynamic landscape of remote work, where connectivity is the lifeline of productivity, LiFi technology emerges as a transformative force, redefining the rules of the game. As remote work setups become increasingly prevalent in today’s world, the demand for...
Why Gamers are Switching to LiFi Technology for Lower Latency
In the ever-evolving landscape of gaming, where split-second decisions can determine victory or defeat, gamers are increasingly turning to LiFi technology for a competitive edge. This blog post delves into the compelling benefits that LiFi offers to the gaming...
Transform Your Internet Experience
Join the LiFi revolution, where unparalleled speed meets unprecedented security.